Corn Sustainability Old
Corn’s Sustainability Story
The corn industry’s evolution in sustainability is documented in the environmental, economic and social improvements over the last several decades and points back to a farmer’s willingness to embrace change.
Most notably, it has meant embracing numerous advancements in technology over many decades which has granted farmers the ability to grow more with less.
As the largest sector in American agriculture corn farmers impact hundreds of thousands of jobs, infuse billions of dollars into the economy and care for our most critical resources, all while seeing substantial improvements in production.
The U.S. Grains Council developed the Corn Sustainability Assurance Protocol (CSAP) in alignment with the National Corn Grower's Association recently articulated corn industry's
Sustainability Commitment
U.S. corn farmers are committed to continuous improvement in the production of corn, a versatile crop providing abundant high-quality food, feed, renewable energy, biobased products, and ecosystem services.
As stewards of the land, we understand the responsibility we have for creating a more environmentally and economically sustainable world for future generations with transparency and through continued advances and efficiencies in land, water and energy use.
The corn industry's commitment to continuous improvement is present throughout the Sustainable Corn Exports platform.
Sustainability Measurement Framework
Sustainable Corn Exports and the U.S. Grains Council’s Corn Sustainability Assurance Protocol use Field to Market: The Alliance for Sustainable Agriculture™ as a key tool to assess the industry’s environmental outcomes.
In particular, Field to Market’s National Indicators Report serves to capture and communicate sustainability trends over time for U.S. agriculture and commodities participating in complex supply chains such as corn.
Field to Market analyzes sustainability metrics focused on U.S. agriculture and the science-based measurements of outcomes associated with commodity crop production, evaluating the conservation and stewardship efforts of our nation’s commodity farmers.
Sustainability Goals Through 2030
Corn farmers are committed to creating a more environmentally and economically sustainable world for future generations with transparency and through continued advances and efficiencies in land, water and energy use.
This commitment is reflected in the National Corn Grower’s Association 2030 sustainability goals.
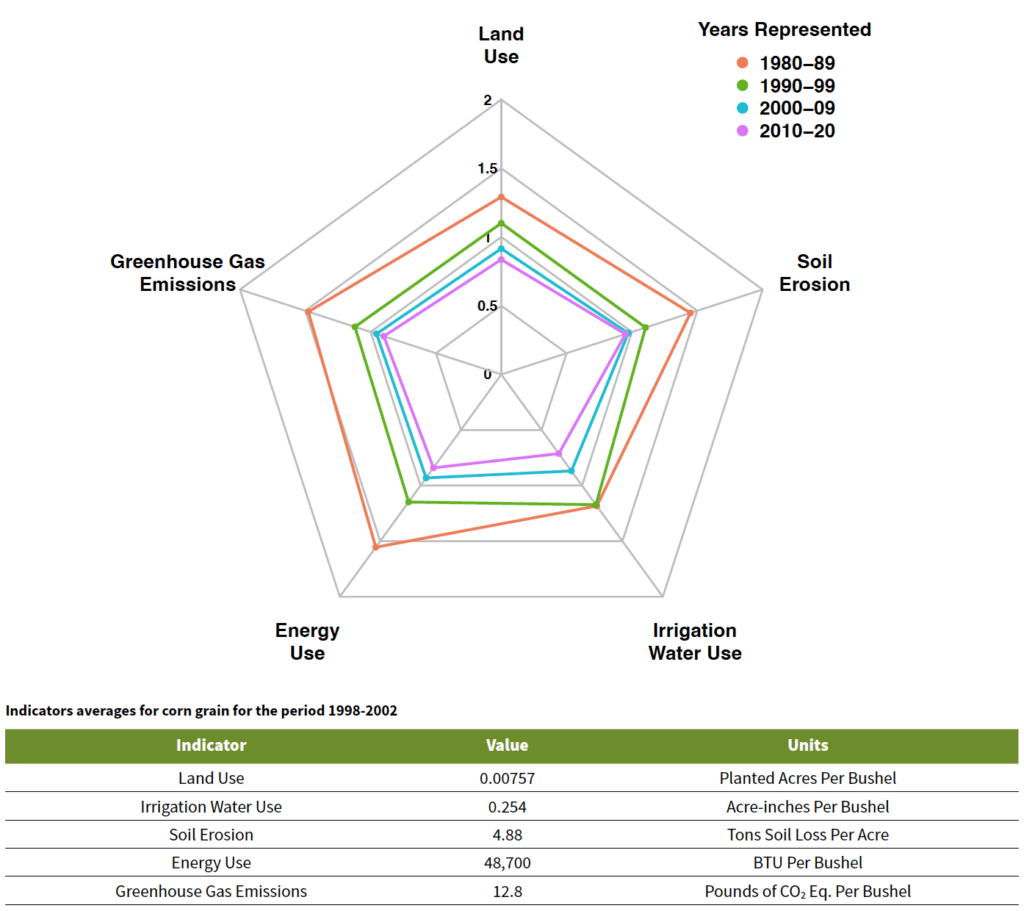
BETWEEN THE YEARS
1980 AND 2020
DECREASED THE AMOUNT OF LAND REQUIRED TO PRODUCE A BUSHEL OF CORN BY 44% EVEN WHILE THE QUANTITY OF CORN PRODUCED HAS INCREASED
REDUCED SOIL LOSS PER ACRE BY 40%
IMPROVED IRRIGATION EFFICIENCIES, LEADING TO PER BUSHEL DECLINES IN IRRIGATION WATER USE OF 56%
IMPROVED ENERGY USE EFFICIENCY PER BUSHEL BY 55%
REDUCED GREENHOUSE GAS (GHG) EMISSIONS PER BUSHEL BY 48%
LOOKING AHEAD TO
2030
INCREASE LAND USE EFFICIENCY BY 12%
REDUCE SOIL EROSION BY 13%
INCREASE IRRIGATION WATER USE EFFICIENCY BY 15%
INCREASE ENERGY USE EFFICIENCY BY 13%
REDUCE GHG EMISSIONS BY 13%
Field to Market
NCGA Sustainability Report